Breast Lumps
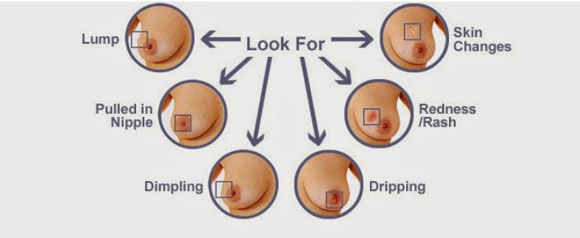
A breast lump is a bulge, protuberance, swelling or bump in the breast or its associated tissues in either or both the breasts. Breast lumps can be benign(non cancerous) or malignant(cancerous). Breast lumps need to be examined as soon as possible through biopsy or other means and identify its malignancy or not.
Inflammation of the breast tissue, known as mastitis, occurs in breastfeeding or lactating women. While nursing, the skin of the nipple is injured or cracked causing the bacteria to enter the damaged area and cause infections. Infections can either be pus growing into an abscess or redness that spreads out as cellulitis.
Due to injuries in a breast, blood vessels can rupture and cause localized swelling.This can further cause death of fat cells thereby causing fat necrosis. Fat necrosis can also happen due to biopsy. There may be a nipple discharge and a dimpling of the skin over the lump.
These are fluid – filled sacs which feel smooth and rubbery under the skin. These are benign in nature and can be painless or painful. Cysts can range in few mm to few cms in size and can cause discomfort based on size as it presses other tissues. Sebaceous cysts can also occur when ducts in the oil glands in the breast get blocked.
Any abnormal growth in the glandular tissue in the breast is an adenoma. Generally fibroadenoma develop in women below 30 years of age. These are round and form with smooth borders and are non cancerous in nature.
Protruding wart like growths developed in the ducts of the breast is referred to as an intraductal papillomas. They are mostly found under the nipple with occasional blood discharge. While women in their fertile age group tend to have multiple such growths, women nearing menopause tend to have just one.
A painless and movable breast lump that is soft and benign is a lipoma. It is non cancerous and fatty tumor.